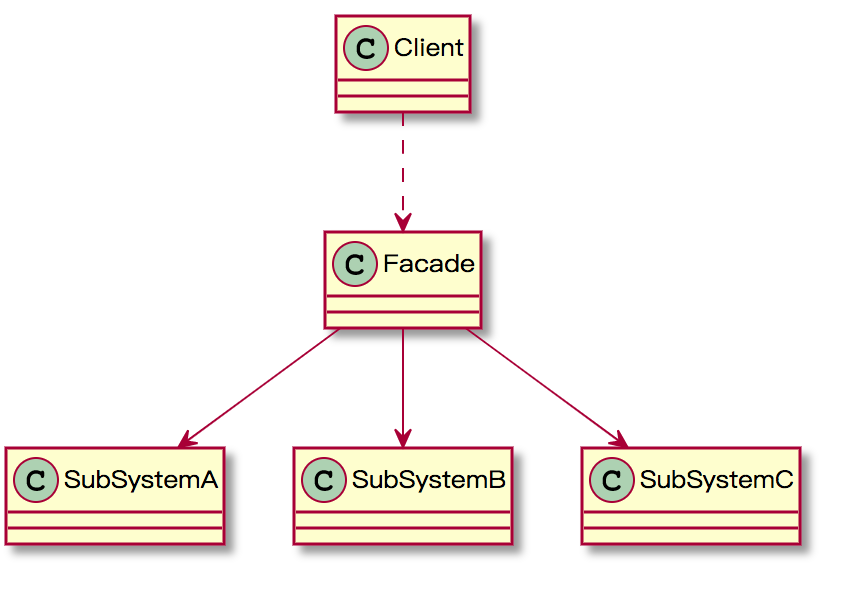
外观模式(Facade Pattern):又称为门面模式,为一组接口提供一个统一的入口。外观模式是迪米特法则的一种具体实现,通过引入一个新的外观角色降低原有系统的复杂度,同时降低客户端类与子系统的耦合度。
Facade(外观角色):外观角色中可以知道相关的多个子系统的功能和责任,客户端调用它的方法,它再传递给相应的子系统对象处理
SubSystem(子系统角色):子系统可以不是单独的类,而是类的集合,它实现子系统的功能,每个子系统都可以被客户端直接调用,或者被外观角色调用,对于子系统而言,外观角色也是一个客户端。
最近习惯了自己做饭,虽然做饭的过程很痛苦,可是看到自己做出来的美食后,还是很幸福很有成就感的。就拿自己做饭吃和去餐馆吃饭来举例,把餐馆看做外观角色,让它把买菜、切菜、炒菜、刷碗这些工作统一组织起来,我要做的就是告诉他要吃什么就行了,下面是示例代码:
SubSystem 类:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 public class BuyVegetable public void buy () LogUtils.i("买菜" ); } } public class CutVegetable public void cut () LogUtils.i("切菜" ); } } public class CookVegetable public void cook () LogUtils.i("炒菜" ); } } public class WashDishes public void wash () LogUtils.i("洗刷刷" ); } }
Facade 类:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 public class Restaurant private final BuyVegetable mBuyVegetable; private final CutVegetable mCutVegetable; private final CookVegetable mCookVegetable; private final WashDishes mWashDishes; public Restaurant () mBuyVegetable = new BuyVegetable(); mCutVegetable = new CutVegetable(); mCookVegetable = new CookVegetable(); mWashDishes = new WashDishes(); } public void eat () mBuyVegetable.buy(); mCutVegetable.cut(); mCookVegetable.cook(); mWashDishes.wash(); } }
Client 类:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 BuyVegetable buyVegetable = new BuyVegetable(); CutVegetable cutVegetable = new CutVegetable(); CookVegetable cookVegetable = new CookVegetable(); WashDishes washDishes = new WashDishes(); buyVegetable.buy(); cutVegetable.cut(); cookVegetable.cook(); washDishes.wash(); Restaurant restaurant = new Restaurant(); restaurant.eat();
有了外观模式,需要交互的类就变成了一个,让它负责和业务类实现交互,简化负责的交互,降低系统的耦合度,但是在标准的外观模式中,如果需要增删改外观类交互的子系统类,就需要改动客户端源码,这样就违反了“开闭原则 ”,因此遇到此类情况需要引入抽象外观类进行优化,还以上面例子为基础:
AbstarctFacade 类:
1 2 3 public abstract class AbstractFacade public abstract void eat () }
ConcreteFacade 类:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 public class NoodlesRestaurant extends AbstractFacade private final BuyVegetable mBuyVegetable; private final CookVegetable mCookVegetable; private final WashDishes mWashDishes; public NoodlesRestaurant () mBuyVegetable = new BuyVegetable(); mCookVegetable = new CookVegetable(); mWashDishes = new WashDishes(); } @Override public void eat () mBuyVegetable.buy(); mCookVegetable.cook(); mWashDishes.wash(); } }
Client 类:
1 2 AbstractFacade abstractFacade = new NoodlesRestaurant(); abstractFacade.eat();
优点
屏蔽子系统,减少客户端所需交互的对象,简化调用
降低客户端与子系统耦合,面对子系统变化,只需要调整外观类即可
子系统间的修改不会相互影响
缺点
不能很好限制客户端直接使用子系统类,对访问子系统类做过多限制则减少可变性和灵活性
设计不当时,增加新的子系统需要修改外观类源码,违背开闭原则
使用场景
需要访问一系列子系统完成业务需求
客户端和多个子系统很高的耦合,使用外观模式解耦,提高子系统的独立性和可移植性
层次化结构中,使用外观模式定义系统中每层的入口,层与层之间不直接产生联系,通过外观类建立联系,降低层之间的耦合

评论